
Have you ever wondered if reading can actually improve your memory? It’s a common question, and one that many people have different opinions on. Well, I’m here to tell you that reading absolutely can improve your memory, and in this article, we’re going to dive deep into why that is and how it works. Whether you’re an avid reader or someone who hasn’t picked up a book in years, you’ll learn just how beneficial reading can be for your memory and overall cognitive health.
When it comes to memory improvement, reading is like a workout for your brain. Just like physical exercise strengthens your muscles, reading exercises your brain and helps keep it in top shape. When you read, your brain is constantly processing information, making connections, and storing new knowledge. This constant mental activity strengthens the neural pathways in your brain, which in turn enhances your memory and cognitive function. So, whether you’re reading a captivating novel, a thought-provoking article, or even this very sentence, you’re giving your brain a good workout and boosting your memory power. In this article, we’ll explore some specific ways that reading can enhance your memory and provide tips on how to make the most out of your reading sessions. So, stay tuned and get ready to unlock the memory-boosting benefits of reading!
This image is property of pbs.twimg.com.
Introduction to the Topic
Reading is a popular and fundamental activity that many people engage in on a regular basis. Whether it’s for pleasure, information, or education, reading plays a significant role in our lives. It enables us to learn, explore different perspectives, and expand our knowledge. But have you ever wondered if reading can actually improve your memory? In this article, we will delve into the topic of reading and memory, exploring the different types of memory, how memory works in the brain, and the potential benefits of reading for memory improvement.
Understanding Memory
Before we delve into the link between reading and memory, let’s first understand what memory is and how it functions. Memory can be defined as the ability to store, retain, and recall information and past experiences. It is a complex cognitive process that involves the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information in the brain.
There are different types of memory, each serving a unique purpose. Short-term memory, also known as working memory, is responsible for holding and manipulating information temporarily. Long-term memory, on the other hand, involves the storage of information for an extended period. Within long-term memory, there are further subdivisions, such as episodic memory (memory of specific events), semantic memory (knowledge-based memory), and procedural memory (memory of how to do things).
Memory works through a series of processes in the brain. When information is perceived, it is initially encoded through various sensory channels. The encoded information is then stored in different regions of the brain. When retrieval is required, the brain retrieves the stored information and makes it available for conscious awareness or use.

This image is property of basmo.app.
The Link Between Reading and Memory
Now that we understand the basics of memory, let’s explore the connection between reading and memory. Numerous research studies have been conducted to investigate the impact of reading on memory.
One study published in the journal “Memory” found that reading enhances both short-term and long-term memory. Participants who engaged in reading activities showed significant improvements in memory recall compared to those who did not engage in reading. These findings suggest that reading can have a positive impact on memory function.
Another study conducted by researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, found that reading fiction can enhance memory and cognitive functions. The study participants were asked to read various types of literature, including fiction, non-fiction, and poetry. The results showed that reading fiction resulted in greater memory improvement compared to other genres. This suggests that the narrative structure and imaginative elements of fiction engage the brain in ways that enhance memory formation.
Benefits of Reading for Memory
Reading offers a wide range of benefits for memory improvement. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Enhancement of Cognitive Functions
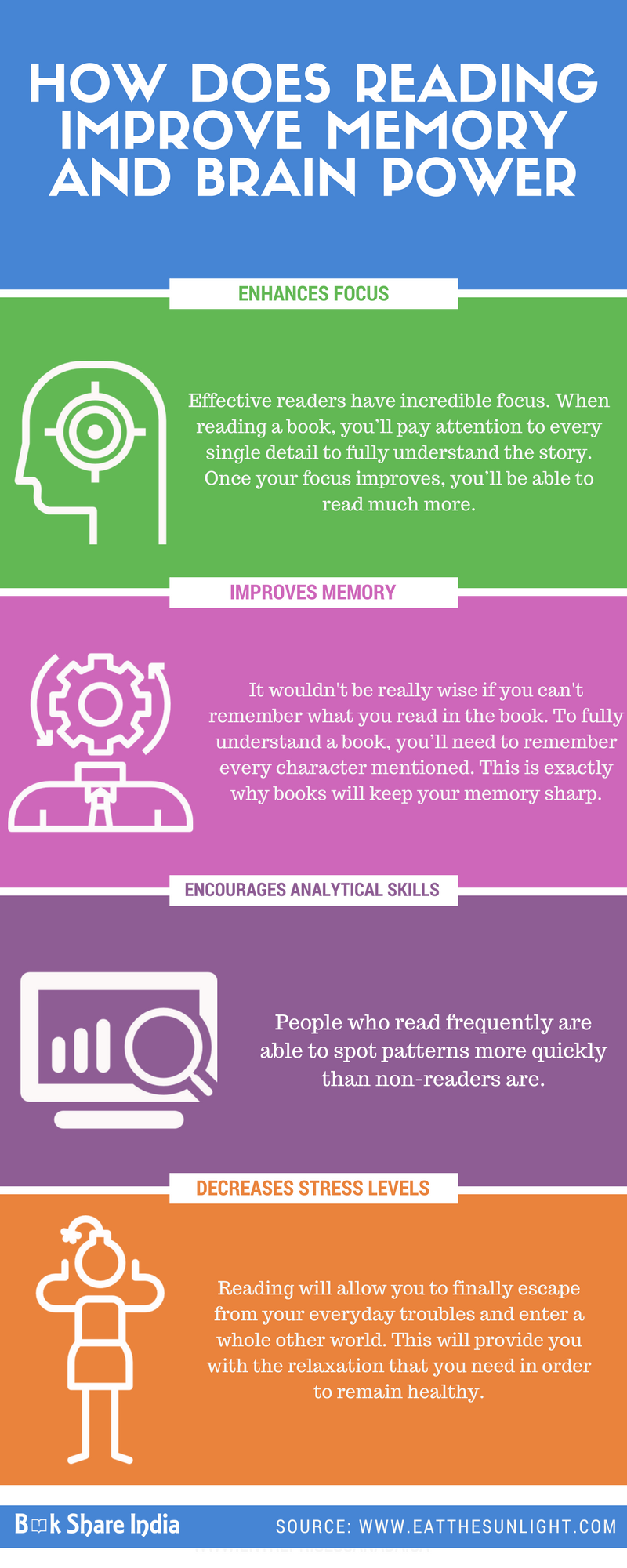
Engaging in reading activities stimulates the brain and enhances cognitive functions, including memory. Reading requires concentration, focus, and active engagement with the material. This mental stimulation helps to strengthen neural connections and improves overall cognitive abilities, including memory.
Formation of Mental Associations
Reading allows us to make connections and associations between various concepts and ideas. When we read, we often encounter new information that we can link to existing knowledge or experiences. These mental associations facilitate memory formation and retrieval. By continuously making these connections through reading, we strengthen our memory networks and improve our ability to recall information.
Improvement in Concentration and Focus
Reading requires sustained attention and concentration. As we read, we need to stay focused on the text, comprehend the information, and follow the narrative or argument. This continuous practice of concentration and focus not only improves reading skills but also helps to strengthen memory processes. It trains the brain to sustain attention, which is essential for memory encoding and retrieval.

This image is property of cdn-infographic.pressidium.com.
Tips to Maximize Reading’s Impact on Memory
To maximize the impact of reading on memory improvement, here are some tips to consider:
Choosing Engaging and Challenging Reading Materials
To derive the maximum benefit from reading, choose materials that are both engaging and challenging. Engaging materials capture your interest and stimulate your curiosity. Challenging materials push your cognitive abilities and encourage active processing of the information. By selecting materials that are both enjoyable and demanding, you can optimize the impact of reading on memory improvement.
Active Reading Strategies
Engage in active reading strategies to enhance memory engagement. Instead of passively reading the text, actively interact with the material. This can involve highlighting or underlining important points, jotting down notes, or summarizing the key ideas. These active reading strategies promote deeper engagement with the material and facilitate memory encoding and retrieval.
Utilizing Memory Techniques
Incorporate memory techniques into your reading practice. Techniques such as visualization, mnemonics, and chunking can help improve memory encoding and retrieval. For example, if you’re reading a book with complex information, try visualizing the concepts or creating mental images to aid in memory formation. Mnemonic devices such as acronyms or creating associations between new information and familiar concepts can also enhance memory retention.
Reading for Specific Types of Memory Improvement
Different types of memory require specific approaches to enhance their improvement. Let’s explore how reading can be utilized for specific types of memory enhancement:
Reading for Vocabulary and Verbal Memory
If you’re looking to improve your vocabulary or verbal memory, reading can be a powerful tool. By exposing yourself to a wide range of written material, you come across new words and expressions. Encountering these new words in different contexts helps to reinforce their meaning and enhance your verbal memory.
Reading for Conceptual Understanding and Memory
Reading complex texts, such as academic journals or philosophical works, can improve your conceptual understanding and memory. These texts often require critical thinking, analysis, and synthesis of information. Engaging with such material challenges your cognitive abilities and strengthens your memory networks for complex concepts.
Reading for Personal Growth and Autobiographical Memory
Reading self-help books, autobiographies, or personal development literature can contribute to personal growth and enhance autobiographical memory. By reading about others’ experiences and insights, you gain new perspectives and practical knowledge. This enriched autobiographical memory can help improve self-awareness, personal growth, and even facilitate memory recall of your own experiences.

This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Alternative Methods for Memory Improvement
While reading is an effective method for memory improvement, there are also alternative approaches to enhance memory function. Here are a few additional methods to consider:
Physical Exercise and Memory
Regular physical exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on memory function. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, stimulates the release of neurotrophic factors, and promotes the growth of new neurons. Incorporating exercise into your routine alongside reading can further enhance memory improvement.
Mental Exercises and Brain Training
Engaging in mental exercises and brain training activities can also boost memory function. These activities, such as puzzles, crosswords, or memory games, challenge your cognitive abilities and promote neuroplasticity. By challenging your brain through various mental exercises, you can strengthen memory processes.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle contributes to overall brain health and memory function. Getting adequate sleep, managing stress, eating a balanced diet, and staying socially active all play a role in memory enhancement. By adopting these healthy habits alongside reading, you create an optimal environment for memory improvement.
Potential Limitations and Cautions
While reading can have numerous benefits for memory improvement, it is important to be aware of potential limitations and practice caution:
Individual Differences in Memory Improvement
It’s essential to acknowledge that individuals may vary in their response to reading and memory improvement. Some individuals may experience more significant memory enhancements compared to others. Factors such as age, existing memory abilities, and overall cognitive health can influence the extent to which reading impacts memory.
Balancing Reading with Other Activities
While reading is a valuable activity, it should be balanced with other activities for a well-rounded approach to memory improvement. Engaging in a variety of cognitive, physical, and social activities can contribute to overall brain health. Balancing reading with other activities helps to maintain a diverse range of cognitive skills and prevents over-reliance on a single activity for memory enhancement.
Avoiding Information Overload
Too much information can overwhelm the brain and hinder memory retention. It’s important to pace your reading and give yourself time to process and consolidate the information. Avoid information overload by breaking down your reading sessions into manageable chunks and allowing time for reflection and consolidation.

This image is property of improvementbuddy.com.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reading has the potential to improve memory function in various ways. By engaging in reading activities, you stimulate the brain, form mental associations, and enhance cognitive functions. Reading can benefit different types of memory, including vocabulary, conceptual understanding, and autobiographical memory. To maximize the impact of reading on memory improvement, choose engaging and challenging materials, implement active reading strategies, and utilize memory techniques.
While reading is an effective method for memory enhancement, it should be complemented by other approaches, such as physical exercise, mental exercises, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to recognize that individuals may vary in their response to reading and memory improvement, and balancing reading with other activities is crucial for a well-rounded approach to memory enhancement. So, why not incorporate reading into your daily routine and reap the numerous benefits it offers for memory improvement? Happy reading!


